In today’s fast-paced world, obesity has become a silent and widespread enemy. From posh neighborhoods to underprivileged communities, its sneaky reach has expanded, leaving no corner untouched.
The statistics are shocking and the consequences, deeply saddening. We now have more people leaning towards the overweight scale than those who are underweight.
The battle isn’t limited to high-income countries anymore. Developing countries are joining the club too, and the situation is alarming.
In 2017 alone, an alarming 4 million lives were cut short as a direct result of being overweight or obese, as reported by the Global Burden of Disease. This isn’t just about appearances or feeling uncomfortable in our own bodies. It’s about life and death.
Obesity is a critical risk factor for chronic diseases like cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, and other metabolic issues.
But there is nothing to fear, because several scientific studies in last couple of years found a secret weapon to fight against obesity: Brown Adipose Tissue(BAT), or as we know it, Brown Fat. This is the story of our journey into the science of obesity and our discovery of the powers of brown fat for weight loss.
Understanding Obesity:
Obesity is the bad guy in our health story. It’s the extra fat in our body that can harm our health. So how do we know if we have too much fat?
This is where the Body Mass Index (BMI) comes in. This is a simple way to measure body fat based on height and weight.
Simply put, it’s your body mass in kilograms divided by the square of your height in meters (kg/m²). A BMI over 25 puts you in the overweight category, and a BMI over 30 means you’re obese.
Understanding Our Metabolic Machinery: The Road to Obesity
The journey towards obesity begins when energy intake exceeds energy expenditure. But what does this mean? To understand, let’s unravel the intricate metabolic processes of our bodies. Our body, essentially a sophisticated energy machine, gets its power from the food and beverages we consume.
These sources of energy undergo metabolism, a biochemical process that breaks down complex food molecules into simple forms, releasing energy that fuels all bodily functions. Two types of metabolic pathways govern this process: catabolic and anabolic. Catabolic pathways involve breaking down molecules to generate energy, whereas anabolic pathways are about building or synthesizing larger molecules from smaller ones, which requires energy. The balance between these two types of pathways is vital to maintain a healthy weight.
If we consistently consume more energy (calories) than our body needs — meaning the energy intake surpasses the energy spent, the excess energy isn’t lost. Instead, our body stores it as fat, mostly in the form of White Adipose Tissue (WAT), a primary contributor to obesity.
Let’s break down the key reasons for obesity:
- Unhealthy Diet: What you eat, how much, and how often you eat, play crucial roles. Are you indulging in balanced meals tailored to your specific needs, or is your diet lacking?
- Lack of Physical Activity: A sedentary lifestyle is a one-way ticket to obesity.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle: This encompasses sleeping habits, stress levels, and even the consumption of alcohol and tobacco.
- Genetics: While genetics may play a role, it’s not the end of the world. Scientists agree that a proper diet, physical activity, and a healthy lifestyle can overcome genetic predispositions.
The Dark Side of Obesity:
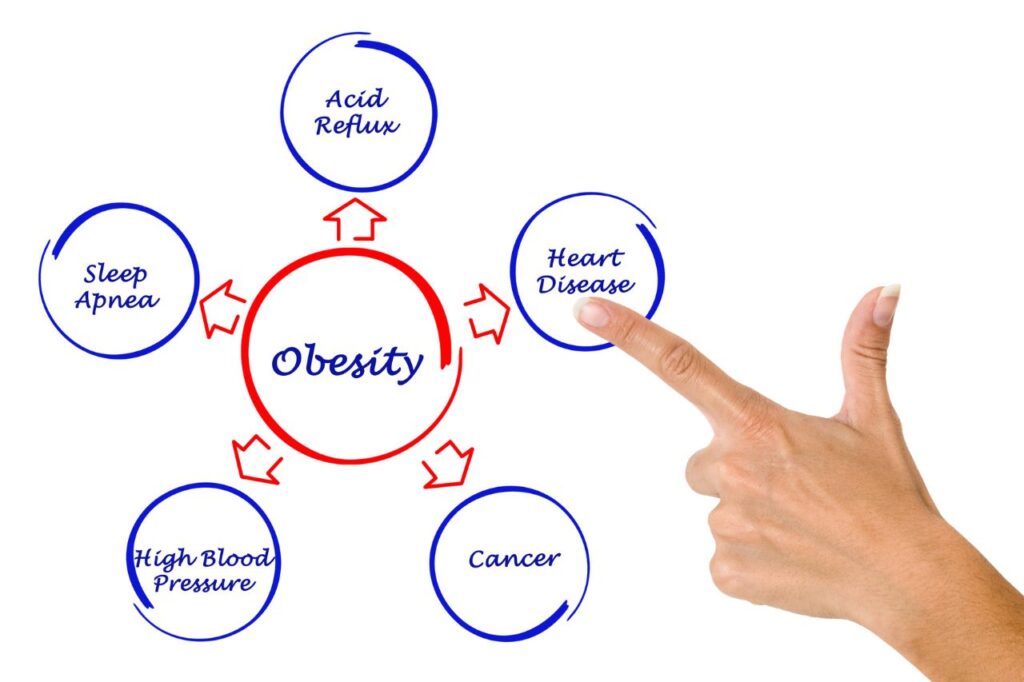
The impacts of obesity extend far beyond the physical appearance. Here’s a snapshot of the health issues it can trigger:
- Heart Disease and Stroke: Extra weight makes you more likely to have high blood pressure and high cholesterol, two major risk factors for heart disease and stroke.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Obesity can affect the way your body uses insulin to control blood sugar levels, increasing your risk of developing diabetes.
- Certain Cancers: Being overweight or obese raises your risk of cancers, including breast, colon, endometrial, kidney, esophagus, and pancreatic cancer.
- Digestive Problems: Obesity increases the likelihood of developing heartburn, gallbladder disease, and liver problems.
Decoding Brown Fat: Science Reveals the Power
Fat is a group of compounds that are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. There are several types of fat, but our bodies primarily contain two types: White Adipose Tissue (WAT) and Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT).
White adipose tissue, the predominant form, stores excess energy as triglycerides (fat cells), contributing to weight gain and obesity. On the other hand, brown adipose tissue, named for its brown coloration due to the high density of mitochondria, plays the heroic role in our tale. When exposed to cold temperatures, BAT springs into action, burning calories to generate heat.
For many years, science considered BAT a physiological feature of newborns and small mammals only. However, studies have uncovered the presence of BAT in adults. Though in smaller amounts, roughly 6.97% of adults possess BAT, located in specific pockets of the body, including the sides of the neck, shoulder, upper arms, and around the collarbone area (source).
BAT’s uniqueness lies in a protein called Uncoupling Protein 1 (UCP1) found in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It’s our natural furnace, capable of generating up to 300 times more heat compared to most other tissues when maximally stimulated (source).
The capacity of BAT to burn fat and enhance energy expenditure makes it a promising tool in the fight against obesity and metabolic disorders. Research paper published in National Institute of Health also expected Brown Fat activation might have huge potential in boost metabolism and maintaining healthy weight (Source)
Igniting the Power of Brown Fat for Weight Loss
Cold Exposure: Exposing our body to cold temperatures is the most natural way to stimulate BAT. This activation is essential to generate heat for maintaining our body temperature. We can definitely feel that while taking a cold shower or turning down the thermostat.
Physical Exercise: Regular physical activity can stimulate the browning of white fat. Various exercises, especially endurance exercises, have shown to increase the levels of a hormone called irisin that promotes the transformation of white fat cells into brown-like cells.
Healthy Diet/ Nutrition: Several researches already found that certain foods and beverages could stimulate brown fat activity. So nutrition plays an important role in activating brown fat which we will explore now.
BAT Activation and Nutrition: The Power of Bioactive Compounds

Let’s explore the bioactive compounds that have shown promising results in activating brown fat.
Resveratrol:
Resveratrol is a polyphenolic compound found in foods such as grapes (primarily in the skins), red wine, peanuts, and certain berries. This compound has received much attention for its potential health benefits. It has been reported to activate sirtuins, a family of proteins that contribute to longevity, and to stimulate the mitochondrial function that can help increase energy expenditure, which in turn may aid weight loss.
In addition to enhancing the activation of brown adipose tissue, resveratrol has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cardioprotective effects. Some research also suggests that it may offer protection against neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. You may explore our research based article on Science Behind The Power of Resveratrol for Weight Loss.
Quercetin:
Quercetin is a flavonoid, a type of plant pigment found in a variety of fruits and vegetables, especially onions, apples, and berries. It has antioxidant properties that can protect the body against oxidative stress. In terms of brown fat activation, quercetin has been shown to stimulate the browning of white adipose tissue, promoting thermogenesis and increasing energy expenditure.
Additionally, quercetin has potential anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and antiviral benefits. Learn more about How Quercetin can support weight loss.
Curcumin:
Curcumin, the primary bioactive substance in turmeric, is well-known for its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Research suggests that it increases the activity of brown adipose tissue and enhances energy expenditure, which can contribute to weight loss.
Furthermore, curcumin may help protect against heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and several types of cancer. You may like to know more about curcumin’s health benefits and weight loss.
Luteolin:
Found in various herbs, vegetables, and fruits, luteolin is a flavonoid recognized for its antioxidant properties. Apart from potentially activating brown adipose tissue, luteolin also exhibits anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and neuroprotective effects.
It might also help inhibit the progression of age-related diseases. Perilla is a great source of Luteolin. Learn more about the scientific research on weight loss benefits of Perilla.
Capsaicin:
Capsaicin, a compound that gives chili peppers their characteristic heat, can activate brown adipose tissue and enhance thermogenesis. It also shows anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anti-cancer properties.
Additionally, capsaicin might improve digestion and promote a healthy metabolism, thereby aiding in weight management. Learn more about our research based article on Power of Capsaicin for Weight Loss.
Berberine:
This compound, derived from several medicinal plants, is known to modulate metabolism and could potentially activate brown adipose tissue. Berberine’s health benefits extend beyond weight management—it exhibits anti-inflammatory, lipid-lowering, and anti-diabetic effects, making it beneficial for metabolic health in general.
Amur Cork Bark is a great source of berberine. It has many health benefits like improving insulin sensitivity, regulating fat production, and enhancing the thermogenic activity of brown fat. Learn more on latest research on Amur Cork Bark’s support in weight loss.
Ginsenoside:
Ginsenosides, active compounds found in ginseng, are associated with a wide range of therapeutic effects. They stimulate the browning of white adipose tissue, contributing to potential weight loss.
Ginsenosides also display anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-cancer activities. White Korean Ginseng is commonly used source of Ginsenosides. Learn more about White Korean Ginseng’s health benefits & weight loss.
Oleuropein:
This phenolic compound, found in olive leaf and olive oil, is suggested to increase brown adipose tissue activity and energy expenditure, which may aid in weight loss.
Oleuropein is also recognized for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-atherogenic, and anti-cancer properties. You may like to know more about how oleuropein activates brown fats and supports weight loss.
Catechins:
These flavonoids, found in green tea, certain fruits, and chocolate, can stimulate brown adipose tissue activity and increase energy expenditure. They also exhibit antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. Green tea extract is a great source of catechins and hope you may like our article on How Green Tea Extract ignites brown fat and supports weight loss.
Ursolic acid:
Present in apple peels, ursolic acid has been shown to stimulate the growth of skeletal muscle and brown adipose tissue, potentially aiding in weight management. Ursolic acid also has anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and potential skin-protection benefits. Holy Basil is a good source of Ursolic acid. You may like to know more about health benefits of Holy Basil and how it supports weight loss.
Propolis:
Propolis, a resinous compound produced by bees, contains flavonoids that have been linked to various health benefits. Research suggests that propolis could stimulate the browning of white adipose tissue, aiding in weight management. Other health benefits include anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-cancer properties. Learn more about health benefits of propolis for weight loss.
Gingerol:
The main bioactive compound in ginger, gingerol, may activate brown adipose tissue and boost metabolism, aiding in weight management. Beyond weight loss, gingerol exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, and may help alleviate symptoms of nausea and digestive discomfort.
Ginger extract is a great source of gingerol. You may find useful our research and evidence based article on weight loss benefits of ginger extract.
Trans-Cinnamic Acid:
Trans-Cinnamic Acid, found in cinnamon, is another compound that could activate brown adipose tissue and improve metabolism. It also shows antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties.
Cinnamon, more generally, may have beneficial effects on blood sugar control, making it a good choice for people with diabetes or prediabetes. Learn more on weight loss benefits of Cinnamon.
Rosmarinic Acid:
Found in rosemary, oregano, and other herbs, rosmarinic acid is believed to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-microbial properties. Some research suggests that it could stimulate the browning of white adipose tissue, though more research is needed in this area.
Caffeic Acid:
Caffeic acid, found in many fruits, vegetables, and in coffee, is a polyphenol that can stimulate brown adipose tissue activity. Beyond weight management, caffeic acid also has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties.
Puerarin:
Puerarin, a compound found in the kudzu plant, has been shown to activate brown adipose tissue. This compound has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for its potential health benefits, which include improving cardiovascular health and alleviating symptoms of menopause. You may like to explore latest scientific research on How Kudzu activates brown fat & supports weight loss.
Each of these compounds has demonstrated potential in activating brown adipose tissue and contributing to weight management. It’s also important to note that they are part of a wide range of fruits, vegetables, and herbs, and that a balanced diet incorporating these foods can provide multiple health benefits beyond weight management.
Harnessing Foods to Activate Brown Fat for Weight Loss
Identifying the compounds that activate brown fat is just one part of the equation. The next logical step is determining the foods that contain these compounds. This knowledge empowers you to make conscious dietary choices, using natural foods or supplements rich in these compounds.
Consider using supplements that contain a higher concentration of these compounds if that fits into your lifestyle. However, it’s important to select high-quality products from trusted brands, ensuring their effectiveness and safety.
Final Thoughts
As we conclude our journey, remember, there are no magic bullets in the battle against obesity. The key lies in embracing a healthy, active lifestyle, nourished by a diet rich in BAT-activating foods or supplements. By understanding and harnessing the power of brown fat, we can all take a proactive approach to our health and weight management. Remember, it’s not just about losing weight — it’s about gaining health.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is brown adipose tissue (BAT)?
Brown adipose tissue, or BAT, is a type of fat in the body that burns energy and produces heat. This is in contrast to white adipose tissue (WAT), which stores energy. BAT is so-named because it is brown due to the high number of mitochondria it contains. These mitochondria give BAT its energy-burning capacity.
2. How does brown fat contribute to weight loss?
Unlike white fat, which stores calories, brown fat burns energy and generates heat. This process is known as thermogenesis. During thermogenesis, the brown fat cells burn calories to produce heat. Therefore, activating brown fat may increase energy expenditure and help with weight loss.
3. Can you increase the amount of brown fat for weight loss?
While research is ongoing, some studies suggest that certain factors, such as cold exposure and certain foods or compounds, can potentially increase the amount of brown fat in the body or boost its activity. Regular exercise and adequate sleep might also influence the amount and activity of brown fat.
4. What foods activate brown fat?
Certain foods and compounds have been linked to increased brown fat activity, including green tea, chili peppers, coffee, and foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids like fish. These foods contain certain compounds, such as catechins, capsaicin, caffeine, and omega-3 fatty acids, respectively, which are known to activate brown fat.
5. Can activating brown fat help combat obesity?
In theory, yes. Activating brown fat increases energy expenditure, which can help burn off excess calories and thereby aid in weight management. However, it’s essential to note that this is only one piece of the puzzle— a balanced diet, regular exercise, and a healthy lifestyle are all crucial for weight management and overall health.
6. How does cold exposure affect brown fat?
Cold exposure is one of the most effective ways to activate brown fat. When your body is exposed to cold temperatures, it needs to generate heat to maintain its core temperature. Brown fat plays a significant role in this process through thermogenesis, where it burns calories to produce heat.
7. What role does exercise play in activating brown fat for weight loss?
Exercise can potentially stimulate the production of a hormone called irisin, which can convert white fat into a form of fat that behaves more like brown fat. This is known as “browning” of white fat. Therefore, regular exercise can potentially boost brown fat activity indirectly and contribute to weight management.
8. Are there supplements that can increase brown fat activity?
Certain supplements contain compounds known to boost brown fat activity. For instance, resveratrol (found in grape skins), curcumin (from turmeric), and capsaicin (from chili peppers) are a few examples. However, supplements should not replace a balanced diet, and it’s always important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
9. Can everyone benefit from increasing brown fat activity?
While research is still ongoing, it appears that most people may benefit from increased brown fat activity in terms of weight management and overall metabolic health. However, the extent of these benefits can vary from person to person, and may be influenced by factors such as age, overall health status, and the presence of certain medical conditions.
10. Are there risks or side effects with activating brown fat for weight loss?
Generally, methods for activating brown fat—like eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and exposing oneself to cold—tend to be safe and healthy. However, some strategies, like taking supplements, might carry risks or side effects for some people, particularly if they interact with medications or exacerbate certain health conditions. As with any health strategy, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider.